Discover a new you with a healthy lifestyle change

Isotonix® Coenzyme Q10
sku C13014
$80.76 CAD
$1.62 CAD Cashback
This product qualifies for free or reduced cost shipping. Learn More
Primary Benefits of Isotonix® Coenzyme Q10
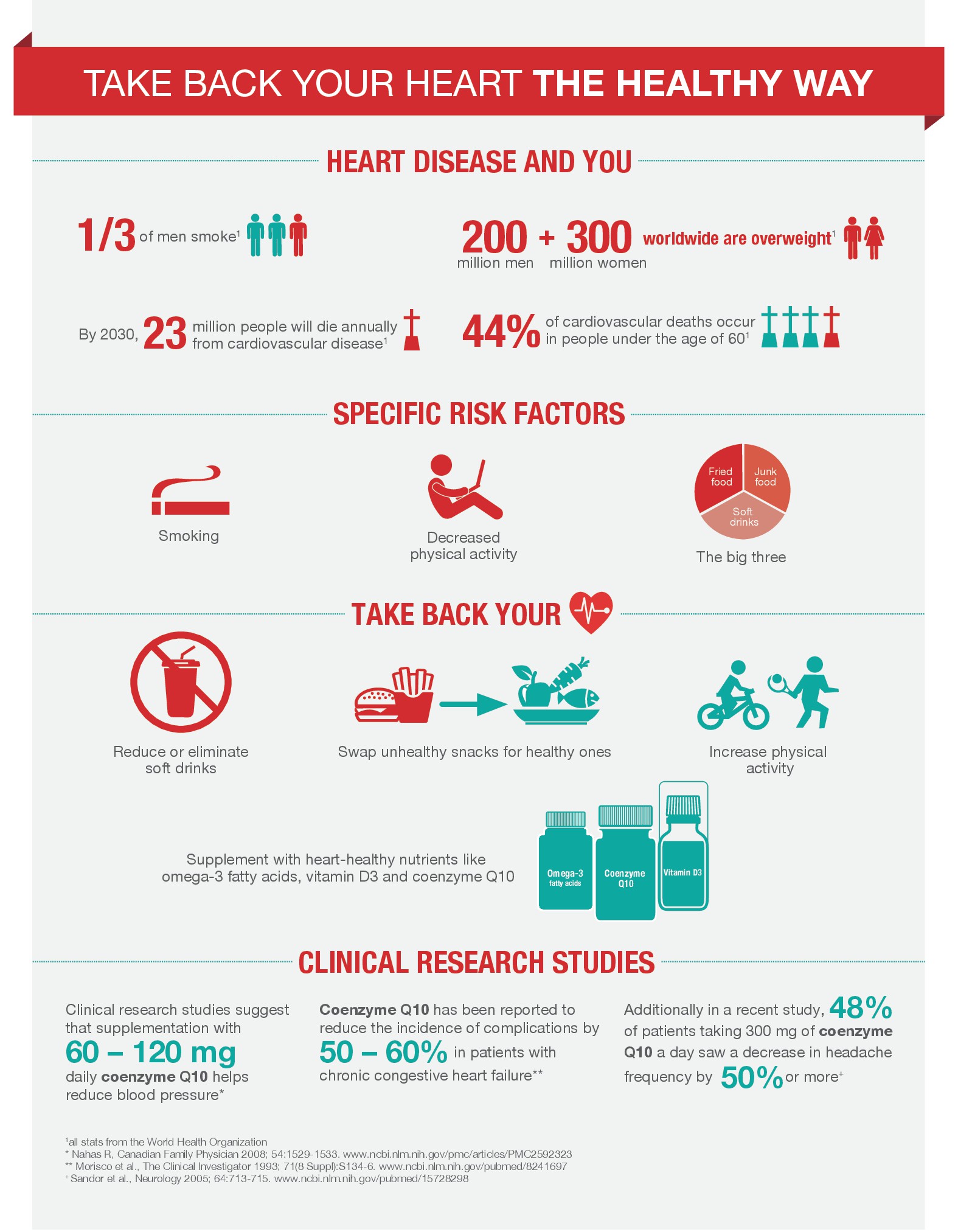
Helps to support and maintain cardiovascular health
- An antioxidant for the maintenance of good health
- Contains 100 mg of Coenzyme Q10
Research shows that CoQ10 is important for the following*
- Supports cellular energy production3,6, 28, 40
- Supports healthy CoQ10 levels3, 36
- Provides antioxidant protection for the cardiovascular system15, 36
- Enhances traditional support of cardiovascular health1, 15, 19, 3
- Helps maintain normal blood pressure2, 6, 18
- Helps maintain heart muscle strength1, 6, 15, 19, 29
- Helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels15, 37
- Promotes head comfort6, 32, 33
- Supports muscle endurance21, 28
- Boosts the immune system6, 12, 13
*The aforementioned has not been approved or considered by Health Canada. The aforementioned are findings made in diverse scientific studies regarding the ingredient CoQ10.

Why the Isotonix® Delivery System is Great!
What Makes Isotonix Coenzyme Q10 Unique?
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a nutrient that plays a vital role in health maintenance. As individuals age, the ability to synthesize CoQ10 begins to decline. Sometimes, this is due to poor eating habits or stress, but the main challenge for most people is the ability to choose the right foods containing CoQ10 as well as get additional nutrients needed to manufacture CoQ10 in the body. Isotonix® CoQ10 contains 100 mg of Coenzyme Q10 to support and maintain cardiovascular health.
Additional research shows that CoQ10 can also support cellular energy production and provide even more benefits for the heart and cardiovascular system. In addition to scientific evidence for the benefits of Coenzyme Q10, Isotonix CoQ10 also boasts absorption and efficiency, due to its isotonic fluid, which helps the nutrients to be absorbed into your system quickly. Isotonic, which means “same pressure,” bears the same chemical resemblance of the body’s blood, plasma and tears. All fluids in the body have a certain concentration, referred to as osmotic pressure. The body’s common osmotic pressure, which is isotonic, allows a consistent maintenance of body tissues. In order for a substance to be absorbed and used in the body’s metabolism, it must be transported in an isotonic state.
Isotonix dietary supplements are delivered in an isotonic solution. This means that the body has less work to do to in obtaining maximum absorption. The isotonic state of the suspension allows nutrients to pass directly into the small intestine and be rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream. With Isotonix products, little nutritive value is lost, making the absorption of nutrients highly efficient while delivering maximum results. Since the antioxidants are in an isotonic solution, it minimizes the chance that important nutrients will be trapped by fats, fibres and tannins, or inactivated by a highly acidic pH level.
Product Classifications
Gluten-Free - The finished product contains no detectable gluten (<10ppm gluten)
No Detectable GMOs - The finished product contains no detectable genetically-modified organisms
Vegan - The product is made without ingredients produced by or derived from animals
Isotonic-Capable Drinkable Supplements - Easy-to-swallow supplements in liquid form are immediately available to the body for absorption
Quality Standards - GMP Operations and Standardised Ingredients
Checked For: Heavy Metals, Microbiological Contaminants, Allergens, Potency, Purity and Identity
Isotonix Delivery System

Isotonix - the World's Most Advanced Nutraceuticals
In addition to scientific evidence for the benefits of Coenzyme Q10, Isotonix CoQ10 also boasts absorption and efficiency, due to its isotonic fluid, which helps the nutrients to be absorbed into your system quickly. Isotonic, which means “same pressure,” bears the same chemical resemblance of the body’s blood, plasma and tears. All fluids in the body have a certain concentration, referred to as osmotic pressure. The body’s common osmotic pressure, which is isotonic, allows a consistent maintenance of body tissues. In order for a substance to be absorbed and used in the body’s metabolism, it must be transported in an isotonic state. Isotonix dietary supplements are delivered in an isotonic solution. This means that the body has less work to do to in obtaining maximum absorption. The isotonic state of the suspension allows nutrients to pass directly into the small intestine and be rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream. With Isotonix products, little nutritive value is lost, making the absorption of nutrients highly efficient while delivering maximum results. Since the antioxidants are in an isotonic solution, it minimizes the chance that important nutrients will be trapped by fats, fibres and tannins, or inactivated by a highly acidic pH level.
Key Ingredients
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 belongs to a family of substances called ubiquinones, and is a water-insoluble, wax-like substance, that is part of the respiratory chain. It is synthesized in the cells, and is involved in electron transport and energy production in mitochondria. In the cellular system, it functions to generate energy from oxygen, in the form of ATP, for bodily processes. CoQ10 also exhibits activity as a free radical scavenger and an antioxidant. The antioxidant activity in the mitochondria and cell membranes protects against peroxidation of lipid membranes. Combining CoQ10 with vitamin E generates a synergistic antioxidant effect on lipoprotein and spares the vitamin E. Coenzyme Q10 can be found in spinach, broccoli, nuts, meats and fish. In the body, it is found in the highest concentration in the cells of the heart, liver, kidney and pancreas. Supplementation of CoQ10 might be beneficial mostly to adults, because the levels of it in the body tend to peak around the age of twenty, and then decline with age. The effects of supplementation with CoQ10 have shown to be especially helpful in maintaining heart health.
Vitamin E
Since vitamin E is one of the most powerful fat-soluble antioxidants in the body, it helps protect cell membranes from the effects of free radicals. Vitamin E works with Coenzyme Q10 for antioxidant protection. High intake of vitamin E have also been found support a healthy heart. Vegetable oils, margarine, nuts, seeds, avocados, wheat germ, and safflower oil are all good food sources of vitamin E. Vitamin E is linked to a healthy heart, enhancement of immune system function and support of healing.
Lipase
Lipase is a fat-digesting enzyme that supports the body’s ability to break down dietary fats into an absorbable form. It is a water-soluble enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of ester bonds in water-insoluble, lipid substrates. Lipase, such as human pancreatic lipase, support the conversion of triglyceride substrates found in oils from food to monoglycerides and free fatty acids. Lipases are ubiquitous in living organisms, and most are built on an alpha/beta hydrolase fold and employ a chymotrypsin-like hydrolysis mechanism involving a serine nucleophile, an acid residue and a histidine. Some lipases also work within the interior spaces of living cells to promote the normal degradation of lipids.
FAQs
- What is Coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10 is actually a two-part compound that is composed of (1) a long, fat-soluble isoprenoid tail that anchors the molecule in the inner membrane of the mitochondria and (2) a quinone that is capable of accepting and transferring electrons through a portion of the respiratory chain. A coenzyme is a non-protein substance that helps enzymes carry out their metabolic function and is not consumed in the reaction. The "Q" stands for quinone and the "10" stands for the number of isoprenoid units in the tail portion of the molecule. Mammals generally have 10 isoprenoid units in the tail portion, but other non-mammalian species may have fewer units. Coenzyme Q10 is a critical biochemical link in the production of energy in the cell. Coenzyme Q10 is found in the cell membranes of all cells in our body, particularly in the inner mitochondrial membranes, and it is especially concentrated in highly active organs such as the heart, lungs, kidneys, spleen, and adrenal glands. The mitochondria produce large amounts of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which helps cells perform work. Since the manufacture of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the mitochondria is known to generate many oxygen radicals, coenzyme Q10 serves an antioxidant function in that location by neutralizing radicals. Coenzyme Q10 also promotes the Kreb's cycle (Citric Acid Cycle), which converts both carbohydrates and fat into usable energy for the cell. Besides these functions within all cells, coenzyme Q10 also works with vitamin E outside of the cell when both compounds are dissolved in circulating low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles carrying cholesterol. These two fat-soluble antioxidants promote arterial health. - What is the source of Coenzyme Q10?
While our livers produce small amounts of coenzyme Q10 and this small amount is distributed to the rest of the body, we get most of this compound from foods such as organ meats, muscle meats, fish, peanuts, spinach, soy, and nuts. In the past it was difficult and very expensive to isolate sufficient amounts of coenzyme Q10 from these food sources for the purpose of dietary supplementation. However, a Japanese company succeeded in synthesizing coenzyme Q10 in 1977, thus making an important nutrient available to the world. - What is a safe and effective dose of supplemental Coenzyme Q10?
A variety of clinical studies has demonstrated that daily servings of as low as 30 mg and as high as 300 mg of coenzyme Q10 are safe and can promote a healthy life. The circulating levels of coenzyme Q10 take about 60-90 days to reach steady state, depending on the serving size taken. Granular coenzyme Q10, as used in Isotonix®, is about equal to the oil-based form in terms of uptake from the small intestine and distribution throughout the body. - If my body makes CoQ10, why should I take a supplement?
When you are young, your body can produce adequate levels of CoQ10. However, as you get older, your cells do not produce enough of the energy they need to function well. Supplementation of CoQ10 has been shown to raise blood levels of this co-enzyme when the body’s ability to synthesize it begins to decrease. - What is the recommended serving size of Coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10 has been used in maintenance servings of 30-60 mg, but can go up to 100 mg or more. - Is there a certain time I should take CoQ10?
Coenzyme Q10 should be taken with a meal containing some fat. Taking it in combination with soy or vegetable oil substantially enhances it absorption. - Is it safe to take CoQ10?
Yes, it is safe to take CoQ10; it does not produce any toxic side effects when ingested by humans. It is listed in the 42nd edition of the Physicians’ Desk Reference as replacement therapy for a nutrient, and no adverse reactions are listed. - Is it okay to take a CoQ10 supplement while pregnant or nursing?
No. The safety of coenzyme Q10 has not been established in pregnancy and lactation. - Is it safe to take CoQ10 while using blood pressure medicine?
If you are currently using blood pressure medication, you should consult your healthcare practitioner before using this product. Discontinue use if allergic reaction occurs.
Science
- Baggio E, Gandini R, Plauncher AC, et al. Italian multicenter study on the safety and efficacy of coenzyme Q10 as adjunctive therapy in heart failure. CoQ10 Drug Surveillance Investigators. Mol Aspects Med 1994;15 Suppl:S287-94.
- Burke BE, Neuenschwander R, Olson RD. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of coenzyme Q10 in isolated systolic hypertension. South Med J 2001;94:1112-7.
- Chan A, Reichmann H, Kogel A, et al. Metabolic changes in patients with mitochondrial myopathies and effects of coenzyme Q10 therapy. J Neurol 1998;245:681-5.
- Chello, M, et al. Protection of coenzyme Q10 from myocardial reperfusion injury during coronary artery bypass grafting. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 58: 1427-1432, 1994.
- Chen Y.F., Lin Y.T. and Wu S.C. Effectiveness of coenzyme Q10 on myocardial preservation during hypothermic cardioplegic arrest. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 107: 242-247, 1994.
- Coenzyme Q10. Monograph. Altern Med Rev. 2007 Jun;12(2):159-68.
- Digiesi, V. et al. Mechanism of action of coenzyme Q10 in essential hypertension. Current Therapy and Research 51: 668-672, 1992.
- Firstein, R. The Nutraceutical Revolution. New York, Riverhead Books, 1998.
- Folkers, K et al. The activities of coenzyme and vitamin B6 for immune responses. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 193: 88-92, 1993.
- Folkers, K. et al. Biochemical rationale and the cardiac response of patients with muscle disease to therapy with coenzyme Q10. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 82: 4513, 1985.
- Folkers, K et al. Coenzyme Q10 increases T4/T8 ratios of lymphocytes in ordinary subjects and relevance to patients having the AIDS-related complex. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 176: 25.
- Folkers, K et al. Coenzyme Q, the immune system and aging. In: Biomedical and Clinical Aspects of Coenzyme Q10. Vol 3. Eds. Folkers, K and Yamamura, Y. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1981, pp. 311-323.Folkers, K. et al. Effect of coenzyme Q10 on serum levels of creatine phosphokinase in preclinical muscular dystrophy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 71: 2098, 1974.
- Folkers, K et al. Effect of Ubiquinone and Related Compounds on Immune Response. In: Biomedical and Clinical Aspects of Coenzyme Q10. Eds. Folkers, K and Yamamura, Y. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1977, pp. 151-163.
- Frei, B, et al. Ubiquinol-10 is an effective lipid-soluble antioxidant at physiological concentrations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 87: 4879-4883, 1990.
- Greenberg, S. and Frishman, W.H. Coenzyme Q10: A new drug for cardiovascular disease. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 30: 596-608, 1990.
- Greenburg S. and Frishman W. Coenzyme Q10: A new drug from myocardial ischemia? Medical Clinics of North America 72: 243-58, 1998.
- Hanaki, Y. et al. Ratio of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to ubiquinone as a coronary risk factor: New England Journal of Medicine, 325: 814-815, 1991.
- Ho MJ, Bellusci A, Wright JM. Blood pressure lowering efficacy of coenzyme Q10 for primary hypertension (review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;(4):CD007435.
- Hofman-Bang C, Rehnqvist N, Swedberg K, et al. Coenzyme Q10 as an adjunctive treatment of congestive heart failure. J Card Fail 1995; 1:101-7.
- Kagan, V, et al. Coenzyme Q: Its role in scavenging and generation of radicals in membranes. In Handbook of Antioxidants, eds. Enrique Cadenas and Lester Packer, New York, Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1996, pp. 157-201.
- Kon M, Tanabe K, Akimoto T, Kimura F, Tanimura Y, Shimizu K, Okamoto T, Kono I. Reducing exercise-induced muscular injury in kendo athletes with supplementation of coenzyme Q10. Br J Nutr. 2008 Oct;100(4):903-9.
- Langsjoen, P.H. et al. Pronounced increase of survival of patients with cardiomyopathy when treated with coenzyme Q10 and conventional therapy. International Journal of Tissue Reactions 12: 163-168, 1990.
- Langsjoen, P.H. et al. A six-year clinical study of therapy of cardiomyopathy with coenzyme Q10. International Journal of Tissue Reactions 12: 169-71, 199.
- Lansjoen, P.H. et al. Response of patients in classes III and IV of cardiomyopathy to therapy in a blind crossover trial with coenzyme Q10. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 82: 4240, 1985.
- Littarru, G.P. et al. Clinical aspects of coenzyme Q: Improvement of cellular bioenergetics or antioxidant protection? In Handbook of Antioxidants, eds. E. Cadenas and L. Packer: New York, Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1996, pp. 203-239.
- Littarru, G.P. et al. Deficiency of coenzyme Q10 in gingival tissue from patients with periodontal disease. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences USA 68: 2332, 1971.
- Lockwood, K. et al. Partial and complete regression of breast cancer in patients in relation to dosage of Coenzyme Q10. Biomedical and Biophysical Research Communications 199: 1504-1508, 1994.
- Mizuno K, Tanaka M, Nozaki S, Mizuma H, Ataka S, Tahara T, Sugino T, Shirai T, Kajimoto Y, Kuratsune H, Kajimoto O, Watanabe Y. Antifatigue effects of coenzyme Q10 during physical fatigue. 2008 Apr;24(4):293-9.
- Morisco C, Trimarco B, Condorelli M. Effect of coenzyme Q10 therapy in patients with congestive heart failure: A long-term, multicenter, randomized study. Clin Investig 1993;71:S134-6.
- Murray, M.T. Encyclopedia of Natural Medicine, Rocklin, CA, Prima Publishing, 1998.
- Nakamura, R. et al. Study of Co Q10-enzymes in gingival tissues from patients with periodontal disease and evidence for a deficiency of coenzyme Q10. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 71: 1456, 1974.
- Rozen TD, Oshinsky ML, Gebeline CA, et al. Open label trial of coenzyme Q10 as a migraine preventive. Cephalalgia. 22:137-141, 2002.
- Sandor PS, Di Clemente L, Coppola G, et al. Efficacy of coenzyme Q10 in migraine prophylaxis: A randomized controlled trial. Neurology. 64:713-715, 2005.
- Shi, H. and Noguchi, N. Dynamics of antioxidant action of ubiquinol: A reappraisal. Biofactors 9: 141-148, 1999.
- Singh R.B. and Singh M.M. Effects of coenzyme Q10 in new indications with antioxidant vitamin deficiency. Journal of Nutritional and Environmental Medicine 9: 223-228, 1999.
- Sobreira C, Hirano M, Shanske S, et al. Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Neurology 1997;48:1238-43.
- Stocker, R. et al. Ubiquinol-10 protects human low-density lipoprotein more efficiently against lipid peroxidation than does alpha-tocopherol. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 88: 1646-1650, 1991.
- Stryer, L. Biochemistry, 2nd ed. New York, W.H. Freeman and Company, 1981.
- Sunamori, M. et al. Clinical experience of coenzyme Q10 to enhance intraoperative myocardial protection in coronary artery revascularization. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy 5: 297-300, 1991.
- Turunen M, Olsson J, Dallner G. Metabolism and function of coenzyme Q. Biochim Biophys Acta 2004;1660:171-99.
Reviews
Displaying 1 - 5 of 8
03/31/2023
by HEE
Quick charge for body battery
My body feel energetic immediately after 120ml of coQ10
Response from Customer Service
07/24/2023
Dear Valued Customer,
Thank you for taking the time to leave your thoughts on Isotonix® Coenzyme Q10. We are happy to hear you are pleased with the product.
Thank you again!
Market Singapore Product Team
07/10/2019
by ANTONIOJ
My review
Great product so far. Great addition to my wellness regimen
06/14/2019
by Anonymous
Thom M
Another great product
05/20/2019
by Anonymous
CoQ10
I love this product and have taken pills for years but much rather take isotonix version. The only negative os that it is only sold in a 30 serving size. Please make a 90 serving size available. It is costly but not as costly as poor health and failing organs. perhaps if you can bottle 90 servings, the cost could be less than 3 times the 30 serving.
12/10/2018
by Anonymous
That is wonderful isotonix .
If need say something that product bottle can be a little big. Thanks
- Prev
- Next